
Menu
Molecular profiling for early patient identification — 1 of 2
Molecular profiling and biomarker-targeted therapy are transforming
patient care in CCA
A genomic analysis revealed that ~50% of patients with CCA had actionable alterations, including FGFR2 fusions or rearrangements13
Potentially actionable genomic alterations are abundant in iCCA14a
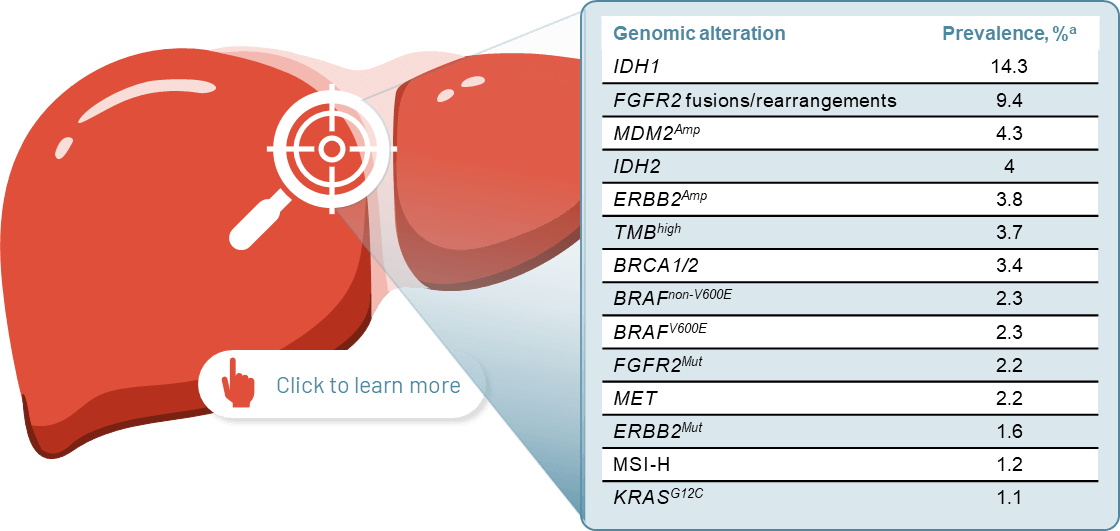
FGFR2 fusions are detectable early in disease progression and are key drivers of tumour growth. Molecular profiling is necessary to identify FGFR2 fusions or rearrangements15,16
Molecular profiling should be performed before or during 1L therapy using NGS12
Figure adapted from Kendre G, Murugesan K, Brummer T, Segatto O, Saborowski A, Vogel A. Charting co-mutation patterns associated with actionable drivers in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J Hepatol. 2023 Mar;78(3):614–26.
aBased on a retrospective analysis of 6,130 patients diagnosed with iCCA from the FoundationCORE database who received diagnostic panel sequencing on the FoundationOne platform. Short variants, fusions/rearrangements and copy number alterations in >300 tumour-associated genes were evaluated, and the TMB and MSI status were available for the majority of the cohort.14
IDH1/2 mutations
- Oncogenic conversion of IDH1/2 is caused by single amino acid substitutions at R132 in IDH1, and either R140 or R172
in IDH214 - These mutations decrease enzymatic activity for oxidative decarboxylation of isocitrate to a-ketoglutarate while also inducing the neomorphic NADPH-dependent reduction of
α-ketoglutarate to the D-2-hydroxyglutarate oncometabolite14
FGFR2 fusions/rearrangements and mutations
- Oncogenic conversion of FGFR2 entails ligand-independent catalytic activation through high-level gene amplification, short variants/indels or generation of fusion proteins14
- In iCCA, the most prevalent mechanism of FGFR2 activation is caused by chromosomal rearrangements that, by juxtaposing exons 1–17 of FGFR2 to sequences contributed by a 3’ partner gene, generate hybrid transcripts encoding constitutively dimerised/active fusion proteins14
ERBB2 amplifications and mutations
- ERBB2 (or HER2) is an oncogenic driver and therapeutic target in several solid tumours14
- While copy number alterations dominate the spectrum of oncogenic ERBB2 alterations, biliary tract cancers harbour a significant proportion of ERBB2 short variants14
BRAF mutations (non-V600E and V600E)
- BRAF belongs to the RAF family of mammalian serine/threonine kinases, which transduce signals downstream of RAS via the ERK/MAPK14
BRCA1/2 alterations
- BRCA1/2 are key components of the DNA damage
repair pathway14
KRASG12C mutations
- Mutationally activated RAS family genes act as key oncogenic drivers in solid malignancies14
MET alterations
- Oncogenic activation of the MET tyrosine kinase receptor can be caused by protein overexpression and genomic alterations, such as gene amplification, exon 14 skipping mutations and fusions14
MDM2 amplifications
- TP53 is targeted for proteasomal degradation by the E3 ligase MDM21
- In several cancer entities, MDM2 is upregulated based on gene amplification, increased transcription and/or
enhanced translation14
TMBhigh
- TMB was developed as a surrogate marker for neoantigen load and predictive biomarker of response to immunotherapy with checkpoint inhibitors14
MSI-H
- MSI is a consequence of genomic instability and is
causally linked to deficiencies in the DNA mismatch
repair machinery14

References

- PEMAZYRE® (pemigatinib). Summary of Product Characteristics. September 2023 (data cutoff: 08 July 2021).
- Rizvi S, et al. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2016;7:789–96.
- Sharma P, et al. Ann Gastroenterol. 2018;31:231–6.
- Ghouri YA, et al. J Carcinog. 2015;14:1.
- Blechacz B. Gut Liver. 2017;11:13–26.
- Valle JW, et al. Cancer Discov. 2017;7:943–62.
- Bañales JM, et al. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;17:557–88.
- Bañales JM, et al. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;13:261–80.
- Bertuccio P, et al. Ann Oncol. 2013;24:1667–74.
- Blechacz B, et al. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;8:512–22.
- Forner A, et al. Liver Int. 2019;39 (Suppl 1):98–107.
- Vogel A, et al. Ann Oncol. 2023;34:127–40.
- Lowery MA, et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2018;24:4154–61.
- Kendre G, et al. J Hepatol. 2023;78:614–26.
- Arai Y, et al. Hepatology. 2014;59:1427–34.
- Borad MJ, et al. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2015;31:264–8.
- Jain A, et al. JCO Precis Oncol. 2018;2:1–12.
- Silverman IM, et al. Cancer Discov. 2021;11:326–39.
- Barr FG, et al. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2016;16:921–3.
- Liu PCC, et al. PLOS ONE. 2020;15:e0231877.
- Abou-Alfa GK, et al. Lancet Oncol. 2020;21:671–84 (data cutoff: 22 March 2019).
- Eisenhauer EA, et al. Eur J Cancer. 2009;45:228–47.
Abbreviations

Sweden API

▼Detta läkemedel är föremål för utökad övervakning. Detta kommer att göra det möjligt att snabbt identifiera ny säkerhetsinformation. Hälso- och sjukvårdspersonal uppmanas att rapportera varje misstänkt biverkning. Se avsnitt 4.8 om hur man rapporterar biverkningar.
Pemazyre (pemigatinib), 4,5, mg, 9 mg, 13,5 mg, tabletter. Rx. EF.
ATC-kod: LO1E N02, antineoplastiska medel, proteinkinashämmare.
Indikation: Pemazyre som monoterapi är indicerat för behandling av vuxna patienter med lokalt avancerat eller metastaserat kolangiokarcinom, med fusion eller rearrangemang av fibroblasttillväxtfaktorreceptor 2 (FGFR2) som har progredieratefter minst en tidigare linjes systemisk behandling.
Kontraindikationer: Överkänslighet mot den aktiva substansen eller mot något hjälpämne som anges i avsnitt 6.1 i produktresumén. Samtidig användning
med johannesört.
Varningar och försiktighet: Permigatinib kan orsaka hyperfosfatemi, svår hypofosfatemi, exudativa näthinneavlossningsreaktioner, torra ögon och ökad serumkreatinin genom att minska renal tubulär sekretion av kreatinin. Samtidig användning av pemigatinib och protonpumpshämmare ska undvikas. Samtidig användning av pemigatinib och starka CYP3A4-hämmare kräver dosjustering. Patienterna ska rådas att undvika att äta grapefrukt och att dricka grapefruktjuice vid behandling med pemigatinib. Samtidig användning av pemigatinib och starka eller måttliga CYP3A4-inducerare rekommenderas inte. Baserat på fynd i en djurstudie och dess verkningsmekanism kan Pemazyre orsaka fosterskador när det ges till en gravid kvinna. Gravida kvinnor ska även informeras om den potentiella risken för fostret. Fertila kvinnor som behandlas med Pemazyre ska avrådas från att bli gravida och män som behandlas med Pemazyre ska avrådas från att göra en kvinna gravid under behandlingen. En effektiv preventivmedelsmetod ska användas hos fertila kvinnor och hos män med fertila kvinnliga partners under behandling med Pemazyre och under en vecka efter avslutad behandling.
Effekter på förmågan att framföra fordon och använda maskiner: Pemigatinib har måttlig effekt på förmågan att framföra fordon och använda maskiner. Biverkningar som trötthet och synstörningar har förknippats med pemigatinib. Försiktighet ska därför iakttas vid framförande av fordon eller användning
av maskiner.
MAH: Incyte Biosciences Distribution B.V. Paasheuvelweg 25, 1105 BP Amsterdam, Nederländerna.
För mer information se www.fass.se.
Senaste datum för översyn av produktresumén: 2023-07-26.
Resources and support

For further information, please refer to the PEMAZYRE Summary of Product Characteristics.1
To request a meeting either for Incyte to contact you or to schedule a visit from an Incyte representative please click here.
To request further medical information, email us at eumedinfo@incyte.com or contact us at our website: https://www.incyte.com/contact-us/medical-information.
